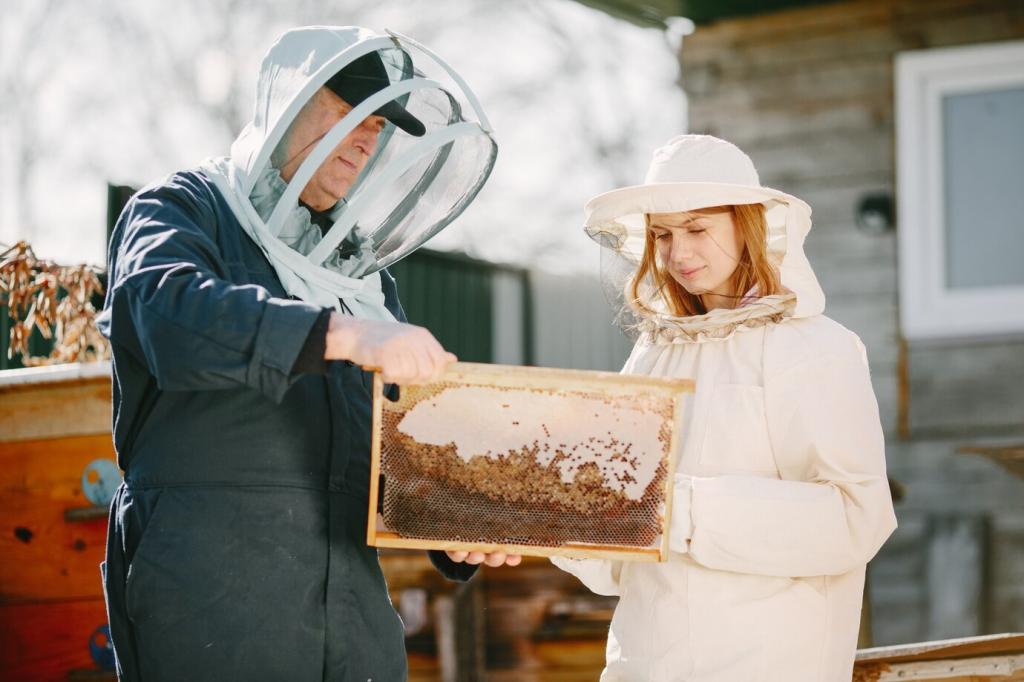
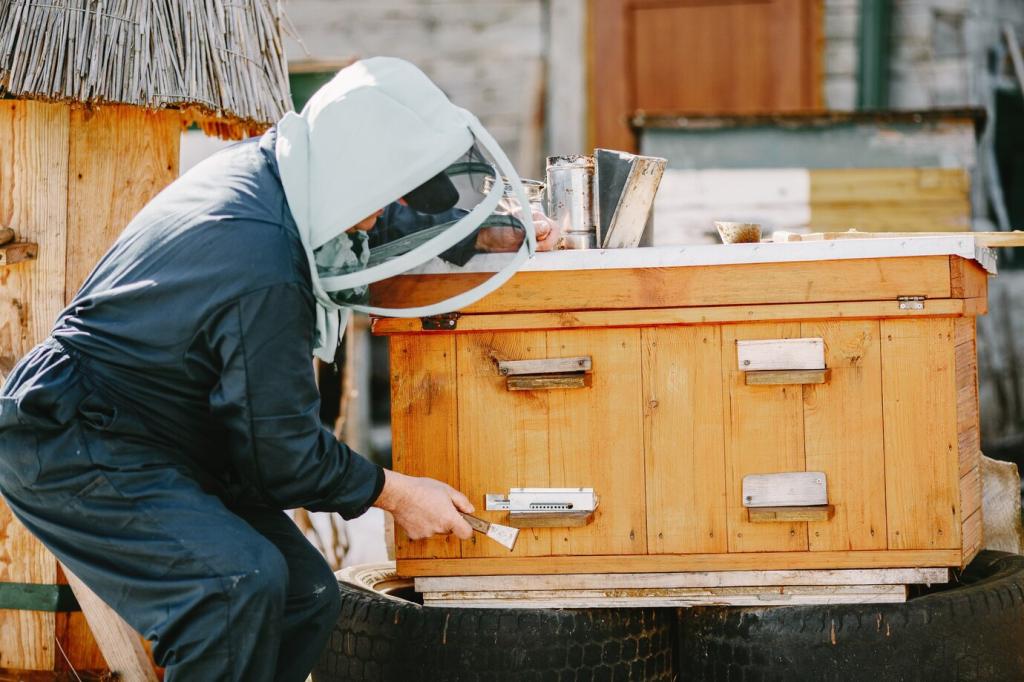
Enhancing Biodiversity Through Urban Beekeeping
Urban beekeeping is rapidly gaining popularity as cities acknowledge the crucial role pollinators play in supporting environmental health and biodiversity. By integrating bees into the urban landscape, communities can actively contribute to stable ecosystems, improve local flora, and create awareness about sustainable living. This page explores how urban beekeeping fosters biodiversity, addresses the benefits for city environments, outlines challenges faced, and offers actionable ways for residents to engage with and support urban pollinators.
The Pivotal Role of Urban Beekeeping in Biodiversity
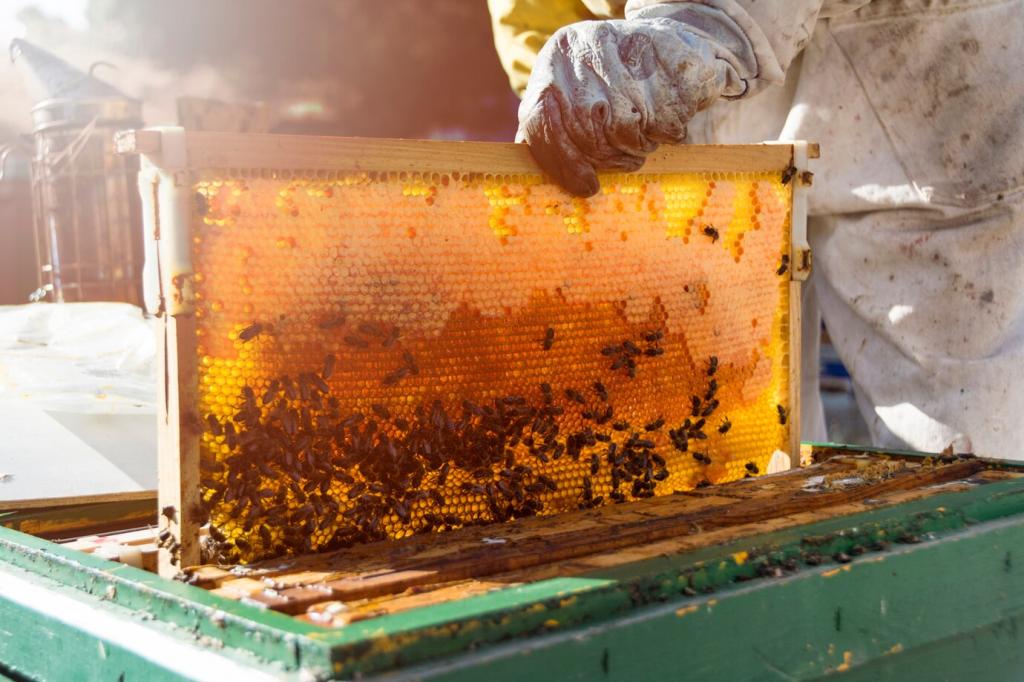

Bees are essential pollinators, driving the reproductive cycles of countless flowering plants within urban areas. By transferring pollen from one blossom to another, bees facilitate the production of seeds and fruits, which are crucial food sources for birds, mammals, and insects. As fewer natural pollinators remain due to habitat loss, urban beekeeping becomes a cornerstone solution, supplementing both wild pollinator populations and ensuring the continuity of urban plant life. This ripple effect enhances the ecosystem, creating interconnected food webs and habitats even in densely populated sectors of the city.
Environmental Benefits of Bees in City Landscapes
Enhancing Urban Agriculture and Food Security
Urban beekeeping profoundly influences local food production. By pollinating community gardens and rooftop farms, bees boost the yield and quality of vegetables, fruits, and herbs. This increased pollination translates to richer harvests, supporting food security initiatives across city neighborhoods and empowering residents to participate in supply chains less reliant on long-distance transportation. A vibrant urban beekeeping culture can thus help establish more self-sufficient and nutritionally diverse urban communities, aligning environmental sustainability with human health.
Promoting Urban Tree Health and Microhabitats
Trees form the backbone of many urban ecosystems, providing shade, cooling, carbon sequestration, and habitats for numerous species. Bees play a crucial role in the reproductive success of flowering urban trees, including maples, lindens, and fruit-bearing varieties. Pollinated trees produce more seeds and fruits, supporting a cascade of wildlife, from songbirds to small mammals. Additionally, healthy tree populations stabilize soil, reduce stormwater runoff, and create a microclimate that makes city living more pleasant, all reinforced by the ongoing activities of urban bees.
Attracting and Sustaining Diverse Urban Wildlife
Pollination stimulates the growth and reproduction of a wide spectrum of plant life, leading directly to more abundant and varied habitats. As bees pollinate flowers, the resulting proliferation of plant species provides shelter, nest-building materials, and food for butterflies, beetles, birds, and other wildlife. These dynamic interactions cascade through the urban food web, supporting ecosystems that can withstand environmental shocks and adapt to urban growth. Bees, therefore, act as a linchpin, indirectly attracting and sustaining many other forms of city dwelling wildlife.